Start with a practical plan: preserve structural bones, add state-of-the-art systems to deliver comfort without masking space’s voice.
Brick walls, steel frames, tall ceilings reveal a story of craft; add state-of-the-art climate control, solar shading, smart lighting, without masking aesthetic.
kalakutsky-inspired detailing yields a unique, originally functional vibe; major choices include reusing brick, matte metal, concrete floors; down lighting reveals daylight streaming down through openings; feet clearance above mezzanines reaching 12 feet.
Focuses on sustainable living: reclaimed timber, low-VOC finishes, LED systems; material budget guides 15–25% upfront premium with payback 3–7 years; energy goals aim for 40–60 kBtu/ft² per year; even now, each sustainable upgrade contributes to occupant comfort, air quality, thermal stability.
Looking for ways to personalize space? Fill exposed volumes with sculture or riempito alcoves; add texture with concrete, timber, brass; focus on sustainable finishes without crowding; take advantage of daylight to reduce down-time and energy use.
Practical Energy Performance Upgrades for Historic Industrial Lofts
Recommended first step: air-seal envelope to cut heat loss by 20–35%; target 0.6 ACH50; verify with blower-door test. wanted outcomes include steadier comfort, reduced heating bills, more flexibility for later upgrades. This yields something tangible in months; savings grow over a full year.
Envelope upgrades include exterior insulation with mineral wool; triple-glazed units with low-emissivity coatings; flush mounting preserves trim; weatherstripping around doors; this combo preserves historic texture while delivering a huge drop in heat gain.
Mechanical core: install a ductless heat pump system for space conditioning; run radiant piping through slabs using copper piping; expects energy-efficient operation, especially in large, open rooms.
Lighting plus appliances: switch to LED fixtures; set smart thermostats; choose ENERGY STAR refrigerators; this trio lowers monthly load.
Creative interior moves: converted spaces in brooklyn bowery neighborhoods into loft-style layouts; dressing zones, dining alcoves, open circulation; ciceros seating blocks create flexible designs.
Materials finishes: carpet surfaces provide warmth; a painter preserves plaster; rustic beams remain visible; copper fixtures highlight piping runs.
Design specifics: large openings with strategic shading keep comfort year-round; however, avoid solar overload in summer by using exterior screens, interior diffusers, or deciduous trees nearby.
Neighborhood note: brooklyn bowery area blends mixed-use blocks; upgrading improves monthly costs; however, compatibility with preservation guidelines required.
Metrics and planning: aim for energy-use intensity drop 20–40% after envelope upgrades; track with monthly bill comparisons; plan for a future solar integration or battery storage in a converted mezzanine or roof-access area.
Envelope Improvements: Windows, Doors, and Insulation for Draft Reduction
Recommendation: triple-pane sealed units with argon fill; warm-edge spacers; weatherstripping on sashes with patterned seals; seal rough openings with continuous foam around jambs; this creates a working envelope that reduces drafts; improves year-round comfort; this approach unlocks possibilities for upgrades within existing frames.
Neighborhood landlords require cost control that yields comfort; select a plan integrating windows, doors, insulation; this approach works on colored facades, whether front street or back street.
photographer golovach notes materials that stay warm; his colored photos show patterned frames on front street facades; use these insights for plans.
Cozy mood relies on well-chosen colored curtains that support air sealing; avoid bulky drapes that intrude on drafts; curtain lining around edges improves performance.
Ornaments on front facades, patterned mullions, inspire practical choices for front windows; use narrow muntins to minimize cold spots; this ripple can trigger revolution in comfort for neighborhood living.
| Component | Recommended Specs | Draft Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | Triple-pane; argon fill; low-E coating; warm-edge spacer; weatherstripping | 40–60% |
| Doors | Insulated cores; multi-point latching; bottom sweep; continuous jamb seal | 30–50% |
| Insulation | Mineral wool or spray foam; cavity fill; exterior rigid boards; taped seams | 50–75% |
Daylighting and Lighting Planning: Maximizing Natural Light and LED Layouts
Install floor-to-ceiling glazing in core production zones alongside smart skylights to maximize natural light, reducing daytime energy use down.
Set daylight targets: daylight factor 2–5% in open floor bays; aim for 300–500 lux on task planes; keep corridors at 100–200 lux.
Glazing area: aim 18–25% of floor area; apply high-reflectance finishes (reflectance 60–70%) to boost daylight distribution; avoid glare with adjustable shading.
LED layout: modular fixtures placed on a grid aligned with vertical columns; CRI above 80; CCT 3500–4100K; daylight-responsive dimming; sensors adjust to exterior daylight.
Open layouts create a colored feeling photographed across brickwork, alongside traditional masonry, telling a story where manufacturing spaces become a stylish living venue.
Move toward a major choice alongside daylight-first planning; vertical fixtures concentrate light where tasks occur, keeping work surfaces well lit while reducing glare.
In manhattan projects, daylight harvesting lowers cooling costs; lighting expenses shrink with dimming tied to exterior brightness; factory floors still run with steady throughput. Concrete brick properties stay visible.
Implementation checklist: measure DF weekly, monitor glazing performance, maintain high-reflectance finishes, verify LED output after seasonal shifts, review piping routes to keep lighting unobstructed. Operator feedback told of improved comfort.
Open spaces in buildings become more livable; light rise into spaces improves mood, supporting throughput.
HVAC Retrofits: Ductless Mini-Splits, Zoning, and Sealing for Comfort
Recommendation: Install a ductless mini-split system with two independently controlled zones; pair with airtight sealing of the envelope; select models with SEER 20–26, HSPF 9–12; refrigerant with low GWP; keep line sets short; ceiling units should be placed to avoid direct drafts on paintings; this approach is well suited for historic spaces filled with character, made to last.
- Envelope sealing plus load planning: going room by room; measure each space; note exposed features such as brick, beams; document paintings; run blower door test; mark leaks; lay out sealing plan including spray foam; caulk at penetrations; this step reduces wasted air; improving comfort across all zones; this approach allows precise control.
- Ductless mini-splits plus zoning: install two to three wall-mounted units; each supports independent setpoints; ensure outdoor condenser sized for local loads; route line sets with minimal length; pick inverter-driven models with SEER 20–26; mount outlets to minimize direct airflow on paintings; wm2k humidity sensors provide feedback to the thermostat; this choice creates quick, predictable comfort while preserving space; airflow impact kept low.
- Zoning strategy: allocate spaces by heat load; living, sleeping, workspace zones; use room sensors; configure occupancy schedules; connect to a smart thermostat; there, a photographer can document changes; still, this allows better control; there is a sense of efficiency irrespective of occupancy.
- Sealing plus insulation: seal around penetrations; install door sweeps; apply silicone at joints; add vapor barrier; target blower door leakage below 0.6 ACH50; 20th century factories offer a model for preserving style; this approach keeps everything usable while protecting historical air flows.
- Historical preservation note: keep exposed elements such as brick walls, timber beams; route lines to avoid visual impact on architectural features; archival notes mention golovach, charows, milliners as 20th century occupants; a photographer can document changes before, during, after; this supports a historical sense there, while modern comfort remains made to last.
- Maintenance plus monitoring: schedule quarterly filter changes; clean coils; check condensate drain lines; use wm2k sensors to monitor humidity; measure temperature; adjust mode settings to minimize impact on original fabric; this maintenance plan include checks for major wear; keeps everything made to last.
Smart Controls and Energy Management: Scheduling, Sensors, and Demand Response

Implement a centralized scheduling engine that uses occupancy signals to control climate, lighting; major loads by time of day, there, this creates predictable energy use, savings.
Emerging sensors provide real-time feedback on occupancy, temperature, humidity, air quality; window status. there, scheduling becomes precise, allowing fine-tuned adjustments that reduce waste, just enough to improve comfort.
Enable demand-response readiness by linking the system to utility signals; this allows rapid reduction of nonessential loads during peak transit periods, contributes time-based savings for owners, residents alike.
In most lofted interiors, where wooden beams meet mason surfaces, a flexible, distinctive control layer rests at the core of this system; it creates a personal, quiet environment, providing a creative, sought-after appeal within apartments, known for huge comfort over time, creating a strong feeling for residents, while entertainment setups remain responsive, energy-aware, with limited waste away from peak spikes.
Measures were seen to support performance via continuous learning; each adaptation followed.
On-site Energy and Storage: Solar, Thermal, and Battery Options for Urban Lofts
Start with a state-of-the-art solar PV array sized 5–7 kW on a roof or patterned façade, paired with 10–15 kWh of storage to maximize daytime efficiency in a loft-style dwelling.
Solar options include roof-mounted PV with microinverters, optimized for limited roof space, minimizing shading near factories, looking at location or nearby neighborhoods such as williamsburg, york.
Solar thermal collectors deliver hot water or space heating; pair with thermal storage using water tanks or phase-change modules to smooth demand.
Battery storage supports solar self-consumption, enabling shift to off-peak power during sleeping hours; install 5–15 kWh modules scaled to occupancy.
Embracing efficiency, smart controllers schedule cooling, water heating, charging around peak sun; spacious lofts citys neighborhoods benefit from this pattern, they keep comfort high.
Before integration, review history of energy use in nearby factories; consider location, sleeping rooms, sculptures in common areas; this would improve efficiency.
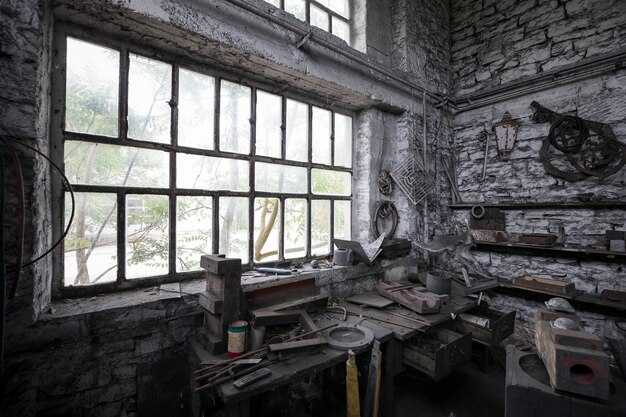
 Loft Industriali – La Perfetta Fusione di Storia e Modernità">
Loft Industriali – La Perfetta Fusione di Storia e Modernità">
 Where to Attend Open-Air Exhibitions in Moscow – Best Venues, Dates & Tips">
Where to Attend Open-Air Exhibitions in Moscow – Best Venues, Dates & Tips">
 Where to Try Local Farm Food in Moscow – Best Farm-to-Table Spots, Markets, and Farms">
Where to Try Local Farm Food in Moscow – Best Farm-to-Table Spots, Markets, and Farms">
 10 Scenic Trail Running Routes Around the World – Discover the Best Trails for Runners">
10 Scenic Trail Running Routes Around the World – Discover the Best Trails for Runners">
 Roaming Numeral – Comprendere il concetto e gli usi pratici">
Roaming Numeral – Comprendere il concetto e gli usi pratici">
 I 10 migliori sentieri escursionistici a Mosca, Idaho – La guida definitiva per le attività all'aperto">
I 10 migliori sentieri escursionistici a Mosca, Idaho – La guida definitiva per le attività all'aperto">
 Dove Visitare Negozi di Piante Ricchi di Verde – I Migliori Negozi di Piante al Mondo">
Dove Visitare Negozi di Piante Ricchi di Verde – I Migliori Negozi di Piante al Mondo">
 I nostri musei preferiti di Mosca fuori dai sentieri battuti, parte 2: gemme nascoste">
I nostri musei preferiti di Mosca fuori dai sentieri battuti, parte 2: gemme nascoste">
 I 21 migliori posti per colazione e brunch a Mosca">
I 21 migliori posti per colazione e brunch a Mosca">
 Foreste magiche per vivere il solstizio d'inverno – Una guida ai boschi invernali incantati">
Foreste magiche per vivere il solstizio d'inverno – Una guida ai boschi invernali incantati">