Zalecenie: launch a regulatory pilot that supports blending traditional therapies with contemporary evidence; a phased design, licensure criteria; safety monitoring; in major urban centers the approach offers learnings that improve patient outcomes, with transparent reporting; the framework should be accessible to clinicians; researchers; patients, образом shaping future policies; фитотерапия comes into scope within regulated product standards.
Differences between regional implementations surface in licensing timelines; data requirements; clinician training; regulatory authorities provide a framework that defines their respective scope, procedures, safety standards; coordination across institutions supports harmonized methods; each jurisdiction keeps its own specifics; eu-wide data-sharing including prospective cohorts helps comparisons.
Upcoming policy shifts aim to align product registration, training, consumer information; based on early pilots, the coming year will specify particular indicators concerning efficacy signals, safety reporting, quality control; researchers should outline methods that are accessible, with harmonized endpoints across sites.
To advance adoption, coordination among universities; clinics; regulators should focus on knowledge transfer; curriculum development; public communication; funding models need to be designed to keep costs accessible; data protection rules must be respected; respective institutions can leverage eu-wide platforms to improve cross-border learning; with transparent performance reports.
For stakeholders, the priority is building a robust evidence base while respecting local traditions; implement pilot networks that compare traditional therapies within a risk-managed framework; ensure outcomes are measurable; aligned with regulatory expectations; the overall approach should provide clear value to patients, physicians, policymakers; thereby guiding scale-up in targeted settings.
Traditional Practices and Their Roots
Begin with registered professionals; this ensures appropriate procedure quality, transparency, accountability. практикующие in regional networks oversee intake, documentation, safety.
Origins trace to folk healers, midwives, monastic circles, local herbalists; teas feature centrally, blending botanical knowledge with rituals; this involves community events.
attitudes shift across generations; many urban residents seek tangible outcomes; regulated training channels exist, limited data. In стране, traditional knowledge remains largely informal, with limited licensing.
From perspectiveleading stance, world scholars explore links between traditional usage; measurable effects are sought. основe data inform guidelines.
example: standardized tea blends, dosing schedules, patient monitoring; labs may track biomarkers.
future trajectory embraces cross-border cooperation; appropriate training, license renewal, patient feedback loops.
Key Traditional Herbs in Russia and Bulgaria: Identification, Uses, and Safe Dosage
Begin with a defined dosage chart from an institute; consult a certified herbalist before use; these guidelines support a measured practise; providers tailor doses based on age, weight, and coexisting conditions. This section targets representative herbs documented in regional traditions; such remedies do not claim cures; they support symptom relief. даёт лечителям базовый ориентир для практики; традиция практии (практики) поддерживает функционально безопасные подходы.
-
Chamomile (Matricaria recutita)
Identification: small daisy-like heads; apple-like aroma; pale yellow petals.
Uses: calming infusion for sleep support; gentle GI comfort; skin soothing with compresses.
Safe dosage: dried flowers 2–4 g per cup; steep 5–10 minutes; максимум 3 cups daily; avoid if known allergy to Asteraceae; caution during pregnancy; consult providers if taking sedatives or thyroid meds. Minimum starting point rests on дave guidelines; минимум 2 g per cup as starter.
-
Yarrow (Achillea millefolium)
Identification: feathery leaves; flat clusters of white to yellow flowers; strong, bitter scent.
Uses: digestive support; topical astringent for minor wounds; anti-inflammatory notes in traditional use.
Safe dosage: dried flowering heads 1–2 g per cup; steep 10 minutes; limit to 2–3 cups daily; avoid during pregnancy; check interactions with anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs. Defined guidance from sources informs cautious practise; education from providers is recommended.
-
Valerian root (Valeriana officinalis)
Identification: woody rhizome with earthy odor; root used in preparations.
Uses: sleep support; muscle relaxation; gentle insomnia relief when used short term.
Safe dosage: dried root 0.5–2 g per cup; steep 10–15 minutes; можно 1–2 cups nightly during initiation; avoid long‑term use beyond several weeks; interactions with sedatives or CNS depressants require supervision. Practice guidelines emphasize gradual titration; источники education support safe dosing.
-
Sage (Salvia officinalis)
Identification: gray‑green oval leaves; woody stems; pungent aroma.
Uses: digestive aid; throat gargles; mild antiseptic notes for mouth rinse.
Safe dosage: dried leaves 1–2 g per cup; decoction 5–7 minutes; maximum 2–3 cups daily; avoid concentrated essential oil ingestion; not recommended in pregnancy or with certain thyroid conditions. Promotes cautious practise; sources recommend monitoring for interactions with antidiabetic meds.
-
Peppermint (Mentha x piperita)
Identification: dark green leaves; strong menthol aroma; purple stems in some varieties.
Uses: GI relief; minor upper respiratory soothing; aromatherapy note in holistic care.
Safe dosage: dried leaves 1–4 g per cup; steep 7–10 minutes; up to 3 cups daily; caution with gastroesophageal refluxDisease; avoid in infants or when using certain antacids; do not ingest essential oil neat. Integrates with Ayurveda approaches as a supporting herb; practitioners advise monitoring dose relative to other meds.
-
Dill (Anethum graveolens)
Identification: slender umbels; feathery leaves; fresh anise scent.
Uses: digestive comfort; seeds used for infusion; potential lactation support in some traditions.
Safe dosage: seeds 1–3 g per cup; steep 10–15 minutes; limit to 2–3 cups daily; avoid excessive use with anticoagulants. Defined guidelines emphasize education of caregivers; providers help determine suitability for infants or children.
-
Calendula (Calendula officinalis)
Identification: bright orange‑yellow petals; daisy‑like flower heads.
Uses: topical wound healing; mild mucosal soothing; ancillary internal use in some regional traditions.
Safe dosage: dried petals 2–4 g per cup for infusion; primarily topical applications; oral use should remain limited; avoid high doses during pregnancy; monitor for allergic reactions. Sources emphasize defined limits; cost‑effective options are common in community clinics.
-
Nettles (Urtica dioica)
Identification: upright nettle with serrated leaves; tiny stinging hairs when fresh.
Uses: mineral support; diuretic properties; traditional tonics for fatigue relief after processing.
Safe dosage: dried leaves 1–2 g per cup; steep 10–15 minutes; limit to 1–2 cups daily during initiation; avoid raw plant foods; monitor for iron interactions in anemic individuals. Representative in many regional herb lists; educational resources from institutes guide safe harvesting and preparation.
-
St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
Identification: vibrant yellow flowers; transparent glands in leaves; distinctive aroma.
Uses: mood support; seasonal adjustment for some individuals; classical notes in traditional psyche care.
Safe dosage: standardized extract 300 mg two to three times daily; avoid with photosensitive drugs, antidepressants, or anticoagulants; interaction risk requires consultation with a clinician or pharmacist. Defined coverage of drug interactions is essential; treat as a cautious, not routine, adjunct.
Complementary modalities such as reiki or reflexology may accompany these botanicals within certified education frameworks; cross‑training remains key to safe practise. For suppliers and practitioners, emphasize cost considerations, appropriate sourcing, and evidence from respected sources; the goal remains to promote safe usage while respecting regional traditions and evolving research. In formal education settings, the institute’s curricula define skill levels; representative providers consistently align dosages with patient needs; education materials stress cautious progression, especially among vulnerable groups. This approach supports a holistic, full‑spectrum care model, where herbal use is one element among broader wellness practises.
Banya, Steam Baths, and Thermal Therapies: Practical Use and Safety
Begin with a safety rule: limit steam sessions to 8–12 minutes; insert a cooling interval; hydrate before, during, or after sessions. Educational note: three core goals are well-being; restore vitality; maintain adequate safety.
Practical practise should occur in controlled settings; limited reliance on DIY approaches; follow information from qualified providers. Temperature ranges in sauna rooms often reach 60–80 percent humidity; keep sessions within the recommended duration.
Safety cues: avoid sessions during acute illness; pregnancy; uncontrolled hypertension; exit immediately if dizziness; chest pain; or headache occurs. Use following guidelines; seek medical input if symptoms appear.
Regulated settings play a role in safety; staff receive training; information should be educational; expatriates rely on official listings.
Herbs may be added; травничество traditions emphasize balance; лечителей guidance были inconsistent between regions; этим caveats apply. Homoeopathy may be pursued as supplementary support; it does not replace diagnostics.
Diagnostics: avoid claims of cures from spa protocols; maintain a clear distinction between well-being goals and диагностики; different regional approaches exist.
Expatriates seeking options may prefer providers in romania; verify licensing; reliance on official listings improves safety. Funding for public educational programmes may be limited; wider dissemination needs stronger funding.
If you wish to explore this path, begin with a three-step plan. Three-step plan: Step one: select a regulated facility; Step two: set three measurable goals; Step three: log maintained detailing timings, responses, herbs employed; any adverse symptoms require medical consultation.
Home Remedies for Common Ailments: Preparation, Dosing, and Cautions
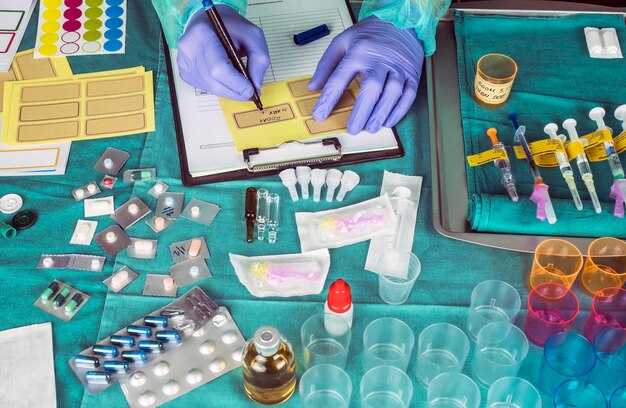
Start with honey lemon tea: steep juice from one lemon in 250 ml warm water; stir in one tablespoon honey; consume two to three times daily during throat irritation or mild cold symptoms. These measures align with objectives for education of consumers в сфере self-care; биоэнерготерапевты show interest in such remedies as initial relief options.
Saltwater gargle preparation: dissolve 1/2 teaspoon salt in 240 ml warm water; rinse mouth for 30 seconds; spit out; repeat 2–3 times daily.
Steam inhalation for congestion: fill bowl with hot water; lean over, cover head with towel, breathe through mouth; duration 5–10 minutes; use once daily if symptoms persist.
Ginger tea for upset stomach: slice fresh ginger 1–2 cm; steep in 250 ml hot water for 10 minutes; drink 1 cup up to 3 times daily; avoid if gallstones or active peptic ulcers.
Peppermint tea for digestion: brew 1 cup; drink as needed; caution for GERD. Headache relief: apply diluted peppermint oil to temples; cool sensation; discontinue if skin irritation.
Cautions: never rely on home remedies as sole care for severe symptoms; seek professional evaluation if fever above 38 C, severe dehydration, vomiting, chest pain, shortness of breath; monitor situations (ситуацию) requiring urgent care; contact emergency services.
objectives include improving literacy regarding self-care; educational materials launched by local networks became long-term resources; focused on differences between home remedies; established clinical guidance; criteria for safe use include age, pregnancy status, allergies; search within academic literature for evidence; osteopathy professionals participate; generations show rising interest; upcoming modules address сфера self-care; responsibility lies with steering consumers toward safe advice; primary aim remains to alleviate everyday discomfort.
Ritual Healing and Community Practices: Methods, Settings, and Social Context
this advice centers on a community-led approach where ritual gatherings deliver cultural meaning, foster mutual aid, provide real relief. A practical strategy is to establish a rotating organization committee that documents decisions in an open, transparent manner. This overview maps located networks from village houses to shared courtyards to ensure accessibility. Reporting is kept concise to improve accuracy while protecting participants. The defined scope includes traditional techniques such as breathwork, singing, herbal remedies, touch-based rituals.
Within open spaces such as community centers, homes, temples, practitioners perform a mix of ritual cleansing, breathwork, singing, drumming, sacred baths, plant-based preparations. These methods rely on sensory cues, rhythm, repetition to stimulate psychosocial alignment, promote somatic relaxation. A trained group of facilitators coordinates these sessions, with trained volunteers plus respected elders sharing knowledge. Settings are located within places of trust, where privacy safeguards exist; local norms guide participation.
Social context features strong intergenerational ties, reputation-based trust, flexible role definitions. Community members often treat authorities with respect; conflicts are managed through mediation circles. источник knowledge rests in local tradition, transmitted through elder circles. Risk mitigation relies on consent lines, opt-in participation, right to withdraw without stigma. момент of transition from collective rite to quiet reflection highlights a real shift. Decisions about participation, duration, scope are documented. Participants report confidently about момент. только qualitative feedback informs воздействие.
To gauge realism of outcomes, organizers collect practical data, such as participant reports of mood, social connectedness, perceived safety. Accuracy of statements is strengthened by triangulation using qualitative notes, short interviews, observer checklists. Results indicate a trend toward increased social belonging, reduced stress markers among small cohorts, faster access to traditional guidance. This overview presents practical approaches that emphasize safety, consent, mutual respect. аналогичное наблюдается в соседних общинах. Воздействие на настроение оценивается качественно через дневники, рассказы участников.
Definition of success in this setting relies on community-defined metrics rather than external benchmarks. that approach aligns with local values, avoids coercion, maintains open channels for feedback. Strategy for scale remains cautious: start with small pilot circles, document lessons in real-time, adjust timing, invite trained observers to verify accuracy. This is a real base for comparable comparisons in future contexts.
Located in diverse settings, facilitators can implement a practical plan: map local circles; craft consent forms; establish referral pathways to formal care when needed; set up an open feedback loop. The organization should maintain a transparent decision log; источник is used to describe where insights originate. объединения местных лидеров структурируют координацию. аналогичное наблюдается в соседних общинах. этой времени исследование фокусируется на долгосрочной устойчивости. даёт clarity about risk control.
Modern Research Methods: How Traditional Practices Are Studied in Labs and Clinics
Recommendation: launch двух-stage research designs to quantify impact of traditional modalities in real-world settings; implement standardized data collection across regional communities; link observed signals with health outcomes; publish findings via governmental channels; some Vienna association coordinated cross-site comparability.
In laboratories, a culturally aware workflow supports reproducibility: use blinded assessments; standardized forms; synchronized scheduling; observational metrics; headaches incidence; pain intensity; fatigue; some datasets indicate эниосуггестивные cues believed to influence reporting; data collection through electronic forms ensures traceability; data passed quality checks when feasible; when feasible, add objective measures such as heart rate variability, skin conductance, physical activity metrics.
They cover diversified clinics; outreach projects; documentation supports cross-site comparison. Several regional datasets contribute to a growing body of evidence on prevalence in communities.
Table below summarizes active study designs across cohorts; clinics; outreach projects. It reflects a growing body of evidence about regionally used modalities; several regional datasets contribute to prevalence in communities.
| Method | Sample Size | Key Outcomes | Notatki |
|---|---|---|---|
| Observational cohort | 320 | headaches prevalence; patient-reported health scores | regional cohorts; data collection through diaries; governmental oversight |
| Physiological metrics study | 120 | HRV; autonomic markers; pain intensity | clinic setting; standardized protocols; data passed quality checks |
| Massage-focused randomized-like trial | 180 | sleep quality; perceived relief | blinded outcome assessors; follow-up at 12 weeks; homeopathy use recorded |
| Qualitative interviews | 40 | perceived efficacy; cultural acceptability | referred by regional association; includes травничество traditions; homeopathy usage noted; эниосуггестивные cues observed |
Audience includes researchers; policy makers; practitioners.
Practical steps: establish cross-border collaboration via a Vienna association; standardize ethics approvals; create data-sharing templates; train staff in cultural competence; ensure privacy; publish annual reports on prevalence; outreach to communities expands audience; monitor health improvements after adoption of integrated approaches.
 Unconventional Medicine in Russia and Bulgaria – Practices and Scientific Research">
Unconventional Medicine in Russia and Bulgaria – Practices and Scientific Research">
 Order Russian Visa Invitation Letter Online | Fast & Secure Processing">
Order Russian Visa Invitation Letter Online | Fast & Secure Processing">
 A Tour of Arbat Street – Moscow’s Most Famous Street">
A Tour of Arbat Street – Moscow’s Most Famous Street">
 Czy mogę zmienić mój plan podróży i odnowić wizę rosyjską? Praktyczny przewodnik">
Czy mogę zmienić mój plan podróży i odnowić wizę rosyjską? Praktyczny przewodnik">
 Visa Support – The Complete Guide to Visa Applications, Documentation, and Processing Times">
Visa Support – The Complete Guide to Visa Applications, Documentation, and Processing Times">
 Do I Need Health Insurance to Travel to Russia Without a Visa?">
Do I Need Health Insurance to Travel to Russia Without a Visa?">
 The Zarengold Private Train – Luxury Private Rail Travel in Russia">
The Zarengold Private Train – Luxury Private Rail Travel in Russia">
 Rosyjska kuchnia wegetariańska – 25 pysznych dań, których musisz spróbować">
Rosyjska kuchnia wegetariańska – 25 pysznych dań, których musisz spróbować">
 Top 10 Winter Activities in Moscow and Saint Petersburg">
Top 10 Winter Activities in Moscow and Saint Petersburg">
 Winter Holidays – Russian Orthodox Christmas Traditions">
Winter Holidays – Russian Orthodox Christmas Traditions">
 Najlepsze miejsca na wypoczynek w Rosji – Gdzie pojechać latem 2019?">
Najlepsze miejsca na wypoczynek w Rosji – Gdzie pojechać latem 2019?">